MOTOR
ANCILIARIES EXERCISE: QUESTIONS ONE NAME:
1. Explain why a ‘blower’ is needed to allow a diesel two-stroke to operate, but not needed on a petrol two-stroke.
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
2. What is the quickest way to stop a diesel engine if the cut off solenoid becomes inoperable?
________________________________________________________________________________
3. Name two purposes of lubrication in a marine diesel engine:
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
4. When started, a cold engine will have a _________ oil pressure which will cause the relief valve to _________.
5. What are 3 possible lubricating system faults?
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
6. What is an indication of a leak in a fresh water cooler tube?
________________________________________________________________________________
7. How can a two-stroke diesel engine use an oil filled ‘wet-sump’ for lubrication, but a two-stroke petrol engine must have a ‘dry sump’ and use other methods to lubricate the engine?
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
ANSWERS ONE
1.
Explain why a ‘blower’ is needed
to allow a diesel two-stroke to operate, but not needed on a petrol two-stroke.
The petrol engine uses the suction in
the sealed crankcase to draw fuel/air into the engine. The diesel need a blower
to force air directly into the cylinder.
2. What is the quickest way to stop a diesel engine if the cut off solenoid becomes inoperable?
Block off the air intake.
3. Name two purposes of lubrication in a marine diesel engine:
Cooling, reducing
friction, removing debris from the action of wear and combustion.
4. When started, a cold engine will have a high oil pressure which will cause the relief valve to open.
5. What are 3 possible lubricating system faults?
No oil, damaged
oil pump, ineffective oil cooler, faulty oil pressure relief valve, engine
wear.
6. What is an indication of a leak in a fresh water cooler tube?
Oil floating
on top of the fresh water in the header tank.
7.
How can a two-stroke diesel engine
use an oil filled ‘wet-sump’ for lubrication,
but a two-stroke petrol engine must have a ‘dry sump’ and use other
methods to lubricate the engine?
The petrol engine uses the sealed crankcase as part of the fuel/air induction
path. The blower on the diesel forces air directly into the cylinder.
QUESTIONS
TWO
1. Describe the problems associated with using raw sea-water to cool a marine engine. (You can list possible solutions to these too, if you wish.)
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
2. Compare skin tank cooling to keel cooling.
(a) Make a list of problems associated with keel cooling pipes, whether in the open or covered with channel. What effect would marine growth have on keel cooling?
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
(b) Does skin tank cooling overcome these problems? Is rust or corrosion a potential problem for skin tanks?
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
3. With heat-exchanger cooling, what precautions must be taken in relation to the raw water path? See the article, Engine water cooling systems.
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
4. What advantage does the air oil cooling system have over a system which uses raw water to cool the oil? Hint: Think about the oil operating temperature. See the article, Lubrication systems.
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
5. State the problem which may be caused if a heat exchanger is too effective, and describe how this problem is normally overcome.
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
ANSWERS TWO
1.
Describe the problems associated with using raw sea-water to cool a
marine engine. (You can list possible solutions to these
too, if you wish.)
Salt-water is highly corrosive. Brass,
stainless or anti-corrosive engine treatments must be used.
Weed and marine animals can block the inlet. Weed traps, strainers, and routine
maintenance keeps them clean.
Metals can be eaten away by electrolytic action in sea water. This problem
is reduced by using special metals and zinc electrodes for protection.
2.
Compare skin tank cooling to keel cooling.
(a) List problems associated with keel cooling pipes, whether in the open or covered with channel.
What effect would marine growth have on keel cooling?
They can be damaged. They penetrate
the hull. Marine growth reduces the cooling efficiency.
(b) Does skin tank cooling overcome these problems? Is rust or corrosion a potential problem for
skin tanks?
Skin tanks are more protected, and do
not penetrate the hull, but they are still less effective with marine growth
on the hull.
3. With heat-exchanger cooling, what precautions must be taken in relation to the raw water path? See the article, Engine water cooling systems.
Must
be kept clean and free of weed and marine organisms.
4. What advantage does the air oil cooling system have over a system which uses raw water to cool the oil? Hint: Think about the oil operating temperature. See the article, Lubrication systems
The
oil can stay at operating temperature, where raw water might cool it too much.
5.
State the problem which may be caused if a heat exchanger is too
effective, and describe how this problem is normally overcome
The engine might be cooled too much.
Thermostats may be used to allow the engine to warm up properly
QUESTIONS
THREE
1(a) Outline the operation of the wet sump force-feed lubrication system. See the article, Lubrication systems
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
(b) If you start an engine with the Caterpillar lubricating system, and the oil pressure gauge reads very high, state what might be the cause of the problem.
________________________________________________________________________________
(c) If you start an engine with the Caterpillar lubricating system, and the oil pressure gauge reads very low, state what might be the cause of the problem.
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
(d) What is the main problem if the oil filter should become blocked due to unsatisfactory maintenance?
________________________________________________________________________________
2(a) What is the function of a sediment bowl or sludge trap, and how does it work?
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
(b)
What contaminants will a sediment bowl collect?
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
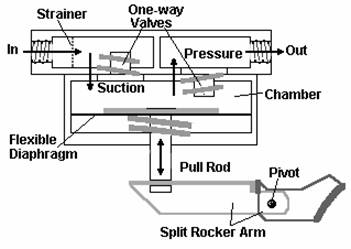
3.
In the diaphragm fuel pump shown above, tick the components which actually
force fuel through the outlet.
Diaphragm and Diaphragm
Spring
Diaphragm and Rocker
Arm Lever
4
Some diaphragm pumps have a glass cover over the top. State two advantages
of using a glass cover, rather than a metal one.
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
5.
What could happen to the lubricating and fuel oil systems if a hole
or split occurred in the diaphragm of a fuel lift pump? (In the diaphragm
fuel pump shown above)
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
6. You suspect that water and muck may have got into the fuel tank through a bad batch of fuel. Where would you open drains and check filters to find out?
Drains:
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
Filters:
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
7. The engine appears to be starving for fuel. Identify the first thing you would check?
Install a pressure gauge and measure fuel pump outlet pressure
a. Check the level of fuel in the tank
b. Check pipes and unions for kinks, damage, leakage and tightness
c. Disconnect the pump and measure fuel flow rate
d. Check filters and strainers
8. “The high pressure output from gear type lubrication pumps is limited to a maximum value by increasing gear clearances!”
TRUE FALSE
9. Tick the most correct statement below:
a. Filters are changed when they begin to show signs of blockage.
b. Filters are changed if a batch of contaminated fuel/oil has been used.
c. Filters are changed when specified by periodic service schedules
d. Filters are changed for all of the above conditions.
10. “Bleeding of diesel fuel systems involves the removal of air from all lines and components starting at the tank end and ending at the injectors!”
TRUE FALSE
11.
If a petrol marine engine stops because sea-water has found it’s way
into the carburettor, what will you most likely have to do?
a. Drain the sludge filters and
re-start the engine.
b. Get out and push-start the
vessel.
c. Drain water from the tank, sludge filters and carburettor bowl, and remove and clean all jets
12. Complete the following statement. “The needle valve and float in the carburettor bowl, is used to:
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
ANSWERS THREE
1.
(a) Outline the operation of the wet-sump force
feed lubrication system
The oil pump draws oil from the sump
and pumps it to the engine through a filter. It flows around the engine galleries
and lubricates all parts. The oil then drains back and collects in the sump
of the engine, ready to be circulated again.
(b)
If you start an engine with this lubricating system, and the oil pressure
gauge reads very high, state what might be the cause of the problem
The oil pump relief valve could be stuck
shut. The oil may be the wrong grade.
(c) If you start an engine with the Caterpillar lubricating system, and the oil pressure gauge reads very low, state what might be the cause of the problem.
No
oil, Worn cylinders, Damaged rings, Damaged oil pump,
very cold, Oil leak.
(d)
What is the main problem if the oil filter should become blocked due
to unsatisfactory maintenance?
The bypass valve will open and feed
unfiltered oil into critical engine components.
2.
(a) What is the function of a sediment bowl or sludge
trap, and how does it work?
Water and muck which is heavier than
the fuel will sink, and collects at the bottom of the filter. From there it
can be removed by undoing a drain valve and draining it into a container.
(b) What contaminants will a sediment
bowl collect?
Water, dirt, metal particles, and anything
heavier than the fuel.
![]() 3. In the diaphragm fuel pump shown in Figure
30, tick the components which actually force fuel through the outlet.
3. In the diaphragm fuel pump shown in Figure
30, tick the components which actually force fuel through the outlet.
Diaphragm and Diaphragm
Spring
Diaphragm and Rocker
Arm Lever
4. Some diaphragm pumps have a glass cover over the top. Can you suggest two advantages of a glass cover, rather than a metal one?
You
can see if the pump is delivering fuel or pumping air. You can see if water
and muck is being pumped from the tank.
5.
What could happen to the lubricating and fuel oil systems if a hole
or split occurred in the diaphragm of a fuel lift pump? (In the diaphragm
fuel pump shown above)
The fuel system and lubricating systems
would contaminate each other through the hole in the diaphragm. This could
show up as diluted lube oil, or clouds of blue smoke form the exhaust.
6.
You suspect that water and muck may have got into the fuel tank through
a bad batch of fuel. Where would you
open drains and check filters to find out?
Drains Filters
Service tanks Secondary fuel filter
Primary
Filters
7. The engine appears to be starving for fuel. Identify the first thing you would check?
a.
Install a pressure gauge and measure fuel pump outlet pressure
b. Check the level of fuel in
the tank
c. Check pipes and unions for kinks,
damage, leakage and tightness
d. Disconnect the pump and measure
fuel flow rate
e.
Check filters and strainers
8. “The high pressure output from gear type lubrication pumps is limited to a maximum value by increasing gear clearances!” FALSE
9. Tick the most correct statement below:
a. Filters are
changed when they begin to show signs of blockage.
b. Filters are changed if a batch of contaminated fuel/oil has been used.
c. Filters are changed when specified by periodic service schedules
d. Filters are changed for all of the above conditions.
10. “Bleeding of diesel fuel systems involves the removal of air from all lines and components starting at the tank end and ending at the injectors!”
TRUE
11.
If a petrol marine engine stops because sea-water has found it’s way
into the carburettor, what will you most likely have to do?
a. Drain the sludge filters and re-start
the engine.
b. Get out and push-start the vessel.
c. Drain water from the tank,
sludge filters and carburettor bowl, and remove and clean all jets
12.
Complete the following statement. “The needle
valve and float in the carburettor bowl, is used to - maintain a relatively
constant fuel level for the jets of the carburettor, to keep the fuel/air
mixture in the correct proportion
Ranger Hope © 2005 (contains reworked material
courtesy of ANTA)